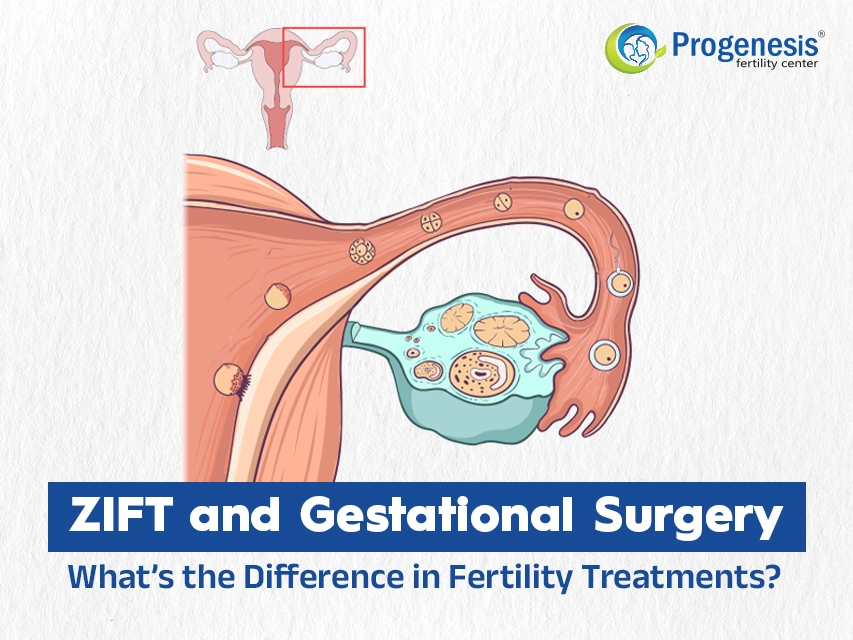
What is ZIFT?
Zygote intra-fallopian transfer (ZIFT), also known as tubal embryo transfer, is similar to IVF. ZIFT is an ART process in which fertilisation takes place in a laboratory. The resulting zygote is subsequently transferred to the mother's fallopian tube via laparoscopy. ZIFT proceeds in the following steps, including, egg removal from the ovaries, fertilisation, and transfer of the zygote into the uterine tubes for implantation and continued development. ZIFT is not suitable for women with abnormal uterine tubes.
What is gestational surrogacy?
Gestational surrogacy happens when a third party bears and delivers a child for a couple or individual. The individual who carries the pregnancy is known as a gestational surrogate or gestational carrier. The couple or individual who wishes to raise the child is known as the intended parents or parent.
The majority of gestational surrogacy pregnancies are carried out using in vitro fertilisation (IVF). In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is the process of creating an embryo in a lab using an egg and sperm from the intended parents or an egg and sperm donor. The embryo is subsequently placed into the carrier's uterus. Because the gestational carrier does not provide the egg, there is no genetic link between the carrier and the child.
Also Read: Blocked Fallopian Tubes? Fertility Plan That Actually Works
Key differences between ZIFT and surrogacy
Here are some key differences between ZIFT and surrogacy:
Carrying of the Pregnancy: The biggest distinction is in who carries the pregnancy. In IVF/ZIFT, the intended mother normally bears her own child, unless her health or medical history forbids her. Surrogacy involves another woman carrying the child on behalf of the intending parents.
Genetic Connection: In terms of genetic connection, ZIFT typically permits both parents to have a biological connection to the child, unless donor eggs or sperm are utilised. In gestational surrogacy, the intended parents can also keep this genetic tie.
Medical Suitability: IVF is great for women who can carry a pregnancy but struggle to conceive normally. Surrogacy is for women who are unable to safely carry a pregnancy, such as those who have a history of repeated pregnancy loss, serious health issues, repeated IVF failures despite the presence of high-quality embryos, or who lack a uterus.
Legal Considerations: Legal factors in IVF are significantly simpler than in surrogacy, which needs formal contracts, compliance with national laws, and, in many cases, legal proceedings to establish parental rights.
Also Read: Guide to Female Infertility: Symptoms, causes & Treatment
When to choose ZIFT or surrogacy
Who is a Good ZIFT Candidate?
Not everyone can use ZIFT; it requires the following factors:
- ZIFT places embryos in the tube, therefore both tubes must be open and functional.
- ZIFT confirms fertilisation in the lab prior to transfer, providing confirmation that the embryo developed.
- Couples who were unsuccessful with IVF or gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) may choose ZIFT as an alteative.
- Some couples may desire ZIFT to be as close to natural conception as possible, with the embryo travelling normally from the tube to the uterus.
Who chooses gestational surrogacy?
Many individuals or couples use gestational carriers to expand their families. A gestational carrier might be needed when:
- A uterine condition has left a prospective parent infertile.
- An intended parent cannot become pregnant or give birth if they have a serious medical or psychological condition that endangers themselves or the fetus.
- A hysterectomy has left a person without a uterus or with a uterine deformity.
- The intended parent is biologically incapable of conceiving or having children, such as a single individual or a gay male couple.
Also Read: Ivf Success Rate & Complications - Surrogacy Treatment
Advantages and challenges of each
ZIFT Advantages:
Confirmed Fertilisation: Before transfer, doctors examine a fertilised embryo to ensure that only viable zygotes enter the body.
Natural Embryo Transport: The embryo's placement in the tube permits it to travel naturally to the uterus.
ZIFT Challenges
Surgical Hazards: The hazards of laparoscopy include anaesthesia, bleeding, and infection.
Requirement for Healthy Tubes: Not recommended if tubes are obstructed, damaged, or scarred.
Recovery Time: Patients may require longer rest following surgery than after IVF transfer.
Gestational Surrogacy Advantages
Parenthood Option: It allows couples or individuals to grow or develop a family even if it is not biologically or physically possible.
Removes Obstacles: This is a dream come true for people who would otherwise be unable to become parents owing to uterine issues, medical or psychological conces, or marital status.
Also Read: IVF Pregnancy with PCOS or Endometriosis
Gestational Surrogacy Challenges
No Guarantee of Pregnancy: There is no guarantee that the pregnancy will be successful or carried to term.
Medication Side-effects: The risks of fertility treatment and medical treatments for the intended parents or carriers.
Financial Risks: Financial risk is related to IVF, medical procedures, legal issues, and compensation.
Emotional Factors: Emotional risk of miscarriage, problems, and other medical disorders.
Other Risks: Frustration over not having control over the carrier, pregnancy, and other circumstances.
Laws and Regulations for Gestational Surrogacy in India
Keep in mind that India has amended its laws and regulations to place some restrictions on illegal surrogacy, such as forbidding commercial surrogacy for foreign couples and only allowing gestational surrogacy for Indian citizens. To prevent exploitation and protect surrogates' rights and interests, rules and regulations have been modified. Furthermore, gay couples and foreign nationals are not allowed to use surrogates. Because laws are susceptible to change, it is always essential to consult with a lawyer to understand the rules and legislation goveing gestational surrogacy in India and, if necessary, in any other country.
Also Read: A Medicinal Boon to Treat Infertility Issues
FAQ’s on ZIFT and
1. What is ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer)?
2. What is GIFT (Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer)?
3. In which conditions are ZIFT and GIFT useful?
GIFT fertiliWhat is the success rate of ZIFT and GIFT?sation occurs in the body rather than in a laboratory dish. This is for couples who want to try natural conception with some aid from specialists.